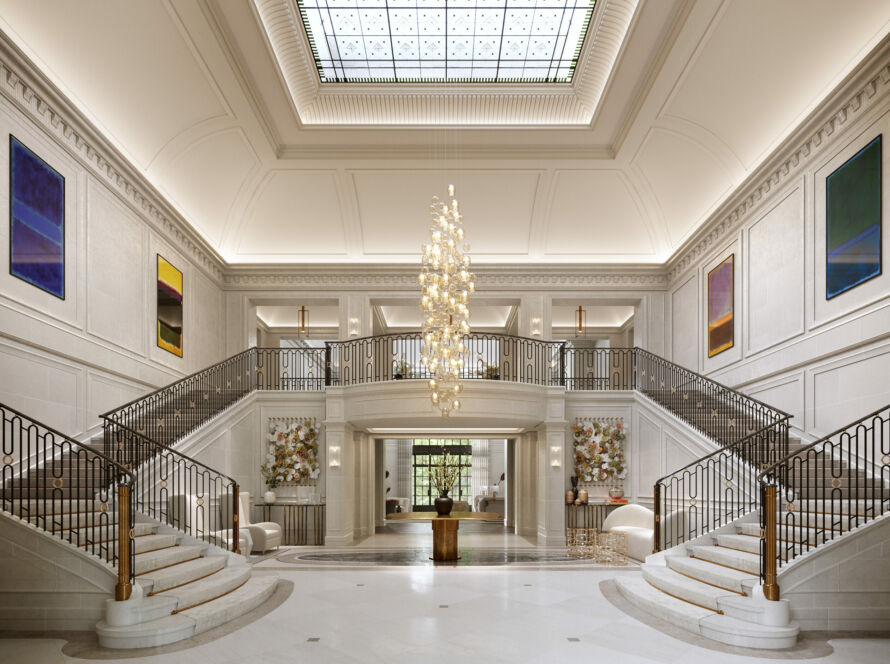
Rendering is the process of creating an image from a set of 3D data. In animation, rendering refers to the creation of each individual frame that makes up the final animation. This can be done using a variety of different techniques, but all involve the use of computers to generate the images. Rendering is an important part of the animation process, as it is what creates the final product that will be seen by audiences. It is a complex process that requires a great deal of care and attention to detail in order to create high-quality images.
What is rendering?
Rendering is the process of creating an image from a model by means of computer programs. It is the last step of 3D animation, after modeling and animation.
Rendering converts a model into an image either by simulating light transport to the eye or by simulating diffuse reflection in the surface of the object. A rendered image may be photorealistic or non-photorealistic.
Rendering is used in computer graphics applications to produce images while animations are running. It is also used to generate shadows for dynamic objects and create special effects such as glows, reflections, etc.
What are the benefits of rendering in animation?
Rendering is the process of creating an image from a set of instructions, or a 3D model. In computer graphics, rendering refers to the generation of an image from a model by means of computer programs.
The benefits of rendering in animation are many. The most obvious benefit is that it allows for the creation of images that would otherwise be impossible to create without the aid of computers. This includes images that are too complex or detailed for traditional methods, or images that require special effects such as those seen in movies.
Another benefit is that rendering can be used to create images that are more realistic than those created with traditional methods. This is because rendering can take into account factors such as lighting and shadows, which traditional methods often cannot.
Finally, rendering can be used to create animations. This is because renders can be created at different frames per second, meaning that they can be played back at different speeds to create an animation.
The different types of rendering in animation
There are three main types of rendering in animation: vector, raster, and 3D. Vector rendering is the process of creating images using mathematical algorithms, which are then converted into a format that can be displayed on a screen or printed. Raster rendering is the process of creating images from a 2D array of pixels, and is typically used for digital photos or illustrations. 3D rendering is the process of creating images from a 3D model, and is used for movies and video games.
How to choose the right type of rendering for your project
There are different types of rendering for different purposes. Here are some factors to consider when choosing the right type of rendering for your project:
- What is the purpose of the render? Is it for final output or for preview purposes?
- What is the level of detail required? Does the scene need to be highly detailed or can it be more simplistic?
- What is the budget for rendering? More complex renders will take longer and require more resources.
- What software will be used for rendering? Some software packages offer specific types of rendering (i.e. Mental Ray in Maya)
- What is the deadline for the project? Rendering times can vary greatly depending on the complexity of the scene.
Keep these factors in mind when choosing the type of rendering for your project to ensure that you get the best results possible.
Conclusion
Rendering is an essential part of the animation process, as it is what gives the final image its polished look. By understanding what rendering is and how it works, you can create better-looking animations that will impress your viewers. With the right tools and techniques, rendering can be a breeze – so get out there and start creating!